
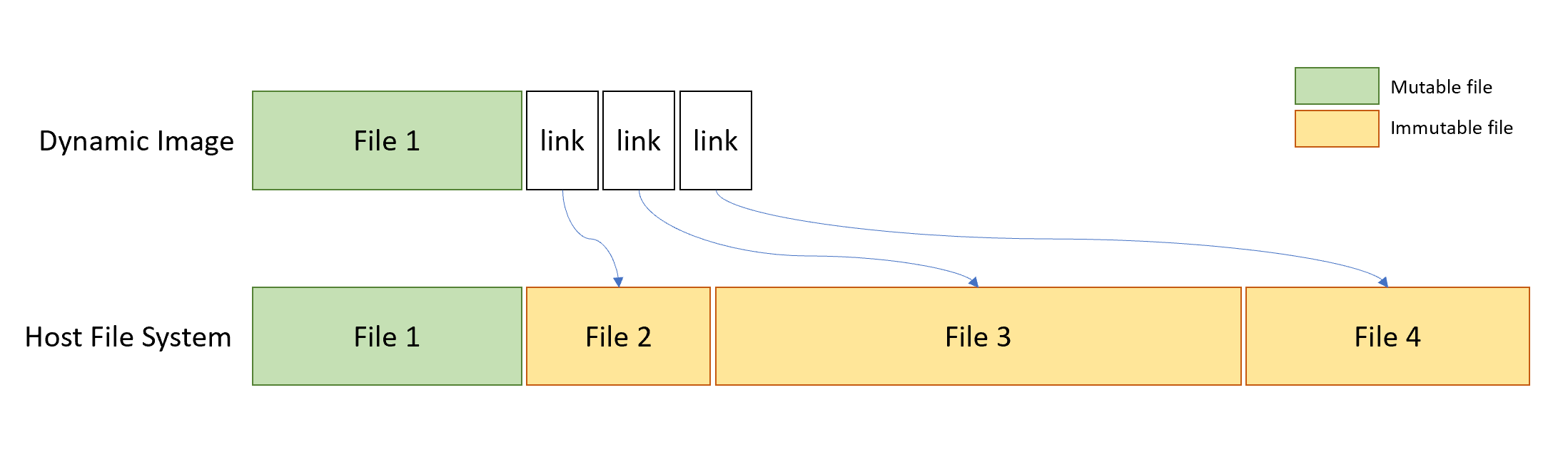
The resulting sandbox presents the best of both worlds: on the one hand, the sandbox is based on Hyper-V technology, which means it inherits Hyper-V’s strict virtualization security. Judging by the accompanying technical blog post, we can say that Microsoft achieved a major technical milestone. The deployment is based on Windows Containers technology.You can configure networking, vGPU, mapped folders, an automated script to run at user login, and many other options. Configurable through a configuration file that has a dedicated format (WSB format).Pristine and disposable – Starts clean on each run and has no persistent state.Integrated part of Windows 10 (Pro/Enterprise).This sandbox has some useful specifications:

Once you are done testing, close Sandbox to remove all data, files, and other items.Two years ago, Microsoft released a new feature as a part of the Insiders build 18305 – Windows Sandbox.Now, run the executable in the same window. Copy the executable file for the application you want to test and paste it into the Sandbox window.Once you have installed or enabled Sandbox, follow these steps to start testing files and applications: Review the prerequisites and retry the installation process. If you don’t see the Sandbox option in the Windows Optional Features tool, your system isn’t eligible to run the application. Finally, look for the Windows Sandbox application on the Start Menu and click to start using it.You may be prompted to restart the system. Locate Windows Sandbox, select it, and then click on OK.Type “Turn Windows Features on or off” on the Start Menu’s search bar and open the Control Panel option which shows up (Windows Optional Features).Once the aforementioned prerequisites are confirmed, follow these steps to install or enable Windows Sandbox:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
